Endoscopes play an important role in minimally invasive medical field, providing image support for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Medical endoscopes, the reliable assistants in the minimally invasive medical field, enter the body through natural body cavities or small incisions, providing doctors with intuitive images to facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment.
▣ History and Development of Endoscopes
The development history of medical endoscopes marks the progress of medical technology. Its history can be traced back to the 19th century, and the development of modern technology has made it one of the indispensable tools for doctors.
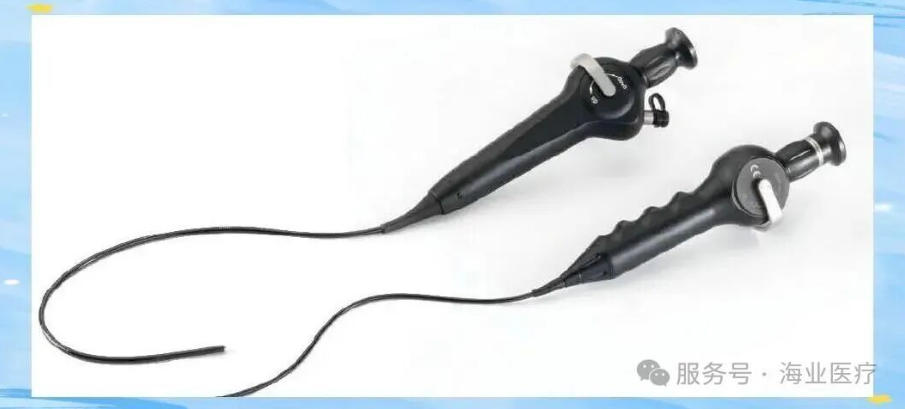

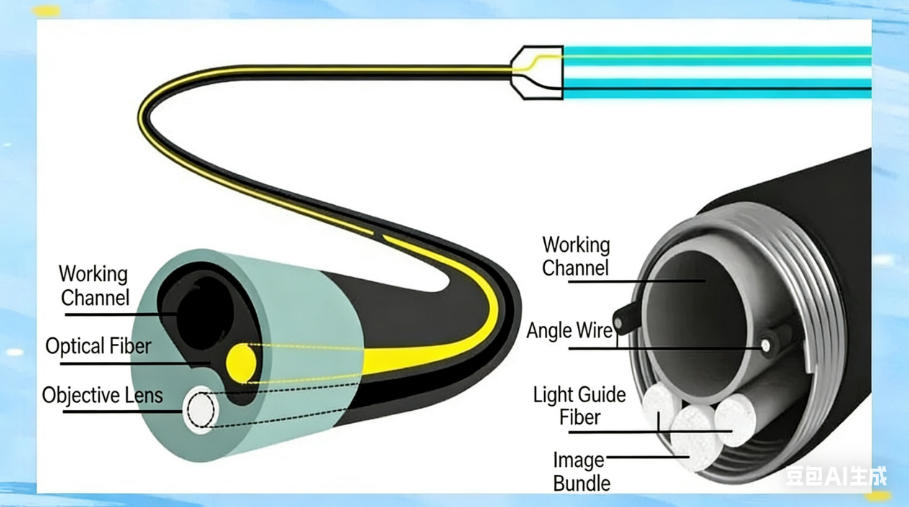
▣ Composition and Characteristics of Flexible Endoscopes
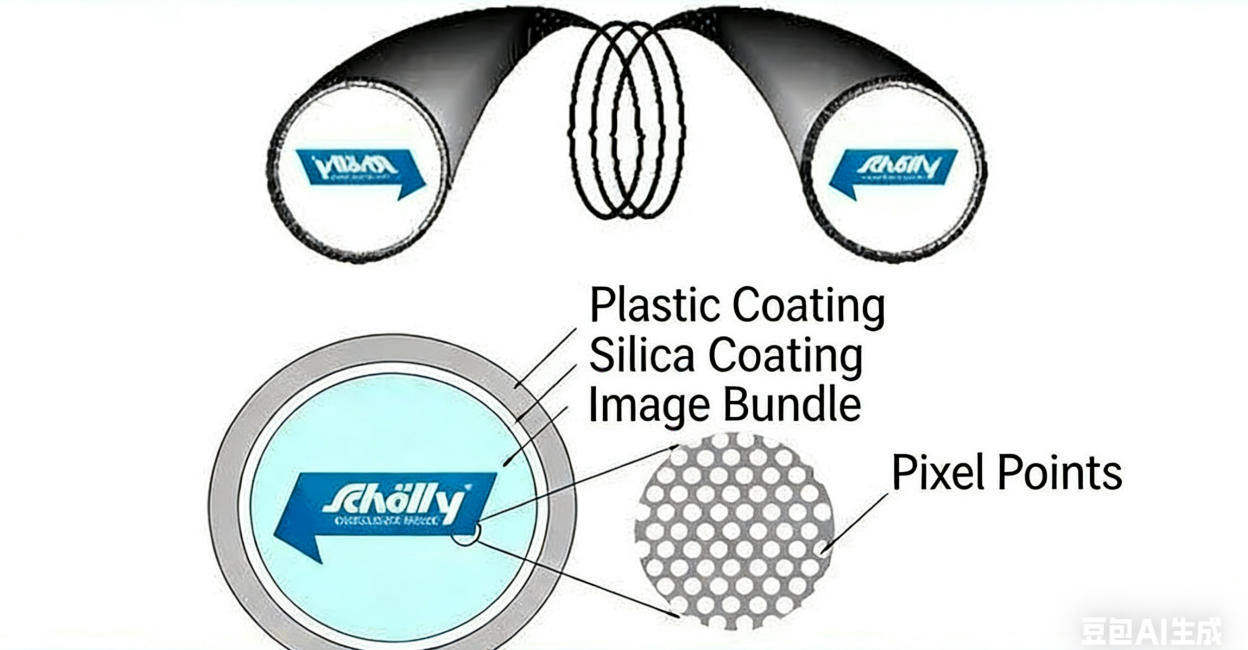
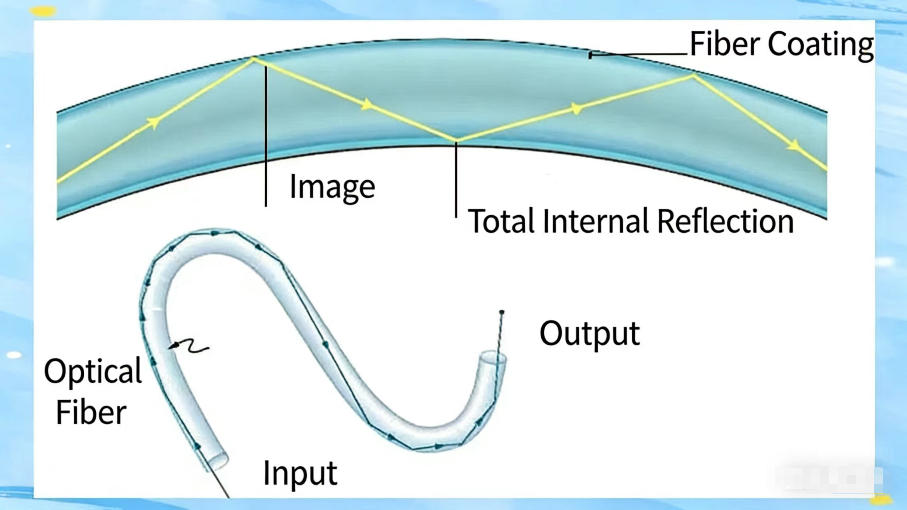
Medical fiber endoscopes have an internal structure that is finely composed of soft fiber image bundles, while the external tube is made of flexible medical materials, enabling the endoscope body to bend flexibly. The image characteristics of this endoscope appear ashoneycomb dots, clear and delicate. It is worth noting that the internal optical system is responsible for transmitting physical images, ensuring the accuracy of diagnosis.
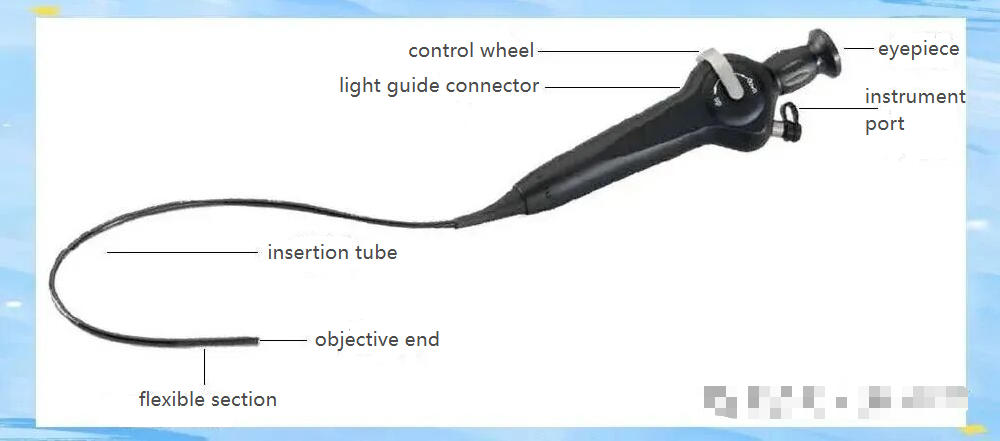
▣ Ophthalmology and Respiratory Applications
Optical flexible endoscopes provide in-depth observation in ophthalmology and respiratory medicine, assist in diagnosis, and help doctors more accurately diagnose diseases in the nasal, pharyngeal, and laryngeal regions.
▣ Gastroenterology and Surgery Applications
In the Department of Gastroenterology, flexible endoscopes are used for the diagnosis and treatment of complex anatomical sites. For example, fiberoptic esophagoscopes, gastroscopes, and cholangioscopes are widely used in the diagnosis of digestive tract diseases, providing doctors with clear images .
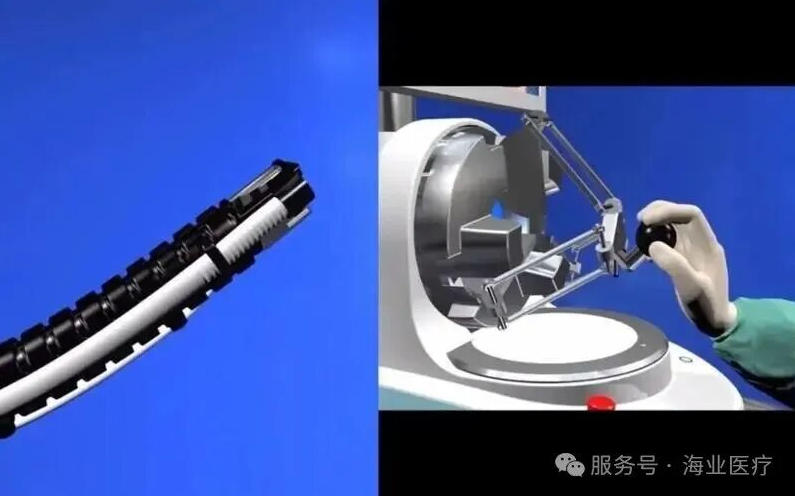

▣ Urology and Gynecology Applications
The application of flexible endoscopes in urology and gynecology provides an intuitive perspective. For example, fiberoptic cystoscopes and fiberoptic fetoscopes in gynecology are indispensable diagnostic tools in their respective departments.
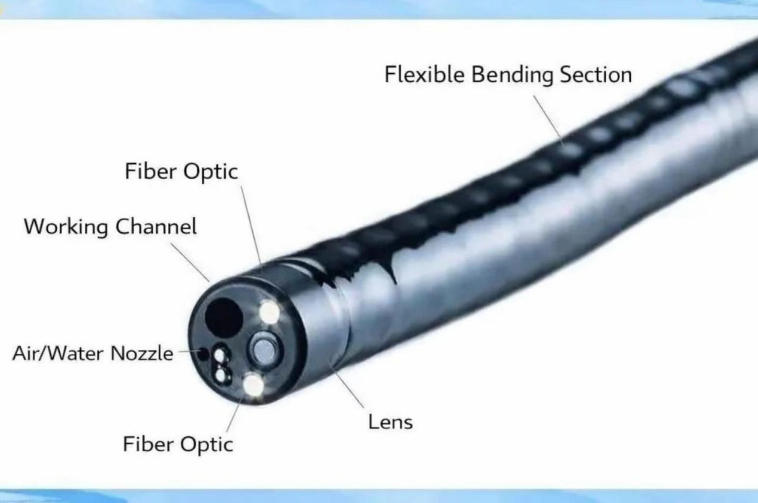

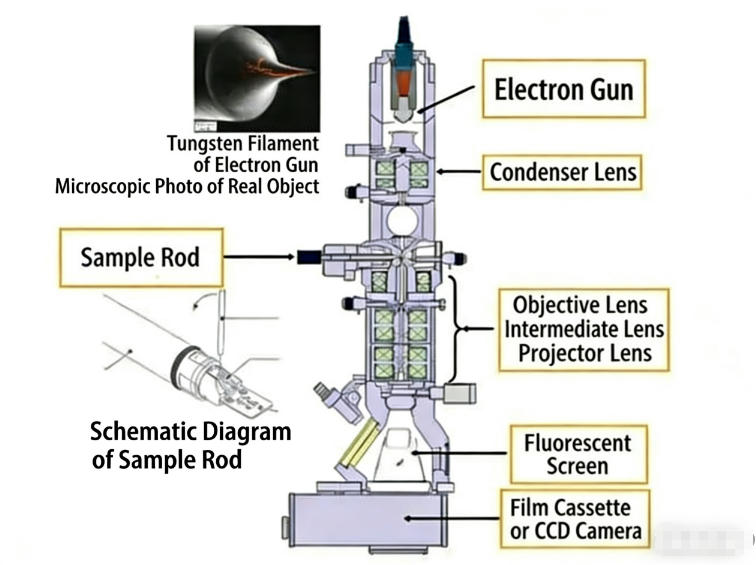
▣ Structure and Function of Electron Microscope
As an electronic endoscope, the core components of an electronic mirror include the CCD/CMOS chip at the tip, the intracavitary light source system, and the mechanical part of the flexible endoscope. The electronic flexible endoscope captures images through the CCD/CMOS chip and transmits digital signals through the endoscope body to provide clear diagnostic images.
▣ Electronic Nasopharyngoscope and Gastrointestinal Endoscope
Electronic nasopharyngoscopes and gastroscopes provide high-definition images, enabling accurate diagnosis. Electronic nasopharyngoscopes are an important tool in the medical field, providing doctors with an intuitive perspective for in-depth observation of the nasal, pharyngeal, and laryngeal regions, while electronic gastroscopes have become a powerful weapon for the diagnosis and treatment of digestive tract diseases.
▣ Endoscopic Ultrasound and Capsule Endoscopy
Endoscopic ultrasound combined with ultrasonic technology provides real-time ultrasound scanning, suitable for more accurate detection and evaluation. Capsule endoscopy, on the other hand, is a convenient way to examine the digestive tract, where patients only need to swallow it with water to easily complete the examination.


Optical mirrors and electronic mirrors differ in their imaging principles.Optical mirror imaging relies on an optical system, and the imaging quality is significantly affected by lighting conditions; electronic mirrors, on the other hand, generate digital signals, providing stable and high-quality imaging.
Disclaimer: This article aims to convey and share industry information and professional knowledge, and is intended solely for personal study, reference, and academic exchange, not for commercial use. All images appearing in this article are reprinted, and due to limited proficiency, there may be issues such as inaccurate interpretations, which only represent the author's personal views.